
The right PVC Pipe Fittings for high-pressure irrigation must match or exceed the system’s maximum operating pressure. These essential Irrigation System Components require materials suitable for specific environmental conditions. Understanding the Difference between UPVC and standard PVC is key to proper selection. Furthermore, knowing How to identify high-quality PVC raw materials in manufacturing ensures long-term performance. This guide helps navigate High-pressure PVC fitting specifications, highlighting durability against stressors like UV exposure and chemical interaction. Users often find significant Advantages of using PNTEK fittings in large-scale irrigation due to their robust design.
Key Takeaways
- Choose PVC pipe fittings that match or exceed your irrigation system’s pressure needs.
- Consider CPVC for higher temperatures, as it performs better than standard PVC.
- Protect PVC pipes from sunlight to prevent damage and make them last longer.
- Use solvent welding for strong, leak-proof connections in high-pressure systems.
- Always check manufacturer specifications to ensure fittings meet your system’s demands.
Understanding High-Pressure Irrigation Demands for PVC Pipe Fittings
Defining High-Pressure in Irrigation Systems
High-pressure irrigation systems operate at elevated water pressures to deliver water efficiently across large areas or through specific types of emitters. While "high-pressure" can vary, it generally refers to systems exceeding 50 pounds per square inch (PSI). Many agricultural and commercial irrigation setups routinely operate between 60 PSI and 100 PSI, and sometimes even higher. These systems often utilize specialized sprinklers or require water to travel long distances, necessitating greater force to ensure adequate coverage and flow. Understanding these pressure requirements is crucial for selecting appropriate components.
Risks of Inadequate PVC Pipe Fittings in High-Pressure Systems
Using inadequate PVC Pipe Fittings in high-pressure irrigation systems poses significant risks. Fittings not rated for the system’s operating pressure can fail catastrophically. This failure often results in sudden bursts or leaks, leading to substantial water loss. Such incidents can damage crops, erode soil, and disrupt irrigation schedules. Beyond immediate failure, inadequate fittings may also experience premature wear and tear due to constant stress. This leads to frequent repairs, increased maintenance costs, and reduced system efficiency. Furthermore, a bursting pipe under high pressure creates a safety hazard for personnel working nearby. Proper selection of robust PVC Pipe Fittings prevents these costly and dangerous outcomes.
Material Considerations for High-Pressure PVC Pipe Fittings
Standard PVC Pipe Fittings vs. Schedule 40/80
Choosing the right material for high-pressure irrigation systems begins with understanding PVC variations. Standard PVC pipe fittings are common for many applications. However, high-pressure systems often require more robust options. Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 PVC pipe fittings offer increased wall thickness compared to standard PVC. This added material directly translates to higher pressure resistance. Schedule 80 fittings have thicker walls than Schedule 40, making them suitable for even greater pressures. Engineers select these schedules based on the system’s maximum operating pressure and required safety margins.
CPVC Pipe Fittings for Higher Temperatures and Pressures
Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride (CPVC) pipe fittings provide superior performance in environments with higher temperatures and pressures. CPVC withstands temperatures up to 200°F, significantly higher than standard PVC. This material also maintains its pressure rating better at elevated temperatures. For example, a 10" CPVC Schedule 80 pipe rated at 230 psi at 73°F would still handle 149.5 psi at 120°F. This resilience makes CPVC ideal for systems where water temperature might fluctuate.
| Operating Temperature (°F) | De-Rating Factor |
|---|---|
| 73-80 | 1.00 |
| 90 | 0.91 |
| 100 | 0.82 |
| 110 | 0.72 |
| 120 | 0.65 |
| 130 | 0.57 |
| 140 | 0.50 |
| 150 | 0.42 |
| 160 | 0.40 |
| 170 | 0.29 |
| 180 | 0.25 |
| 200 | 0.20 |
The material’s inherent properties, like its higher glass transition temperature (Tg) and heat deflection temperature (HDT), explain this enhanced performance.
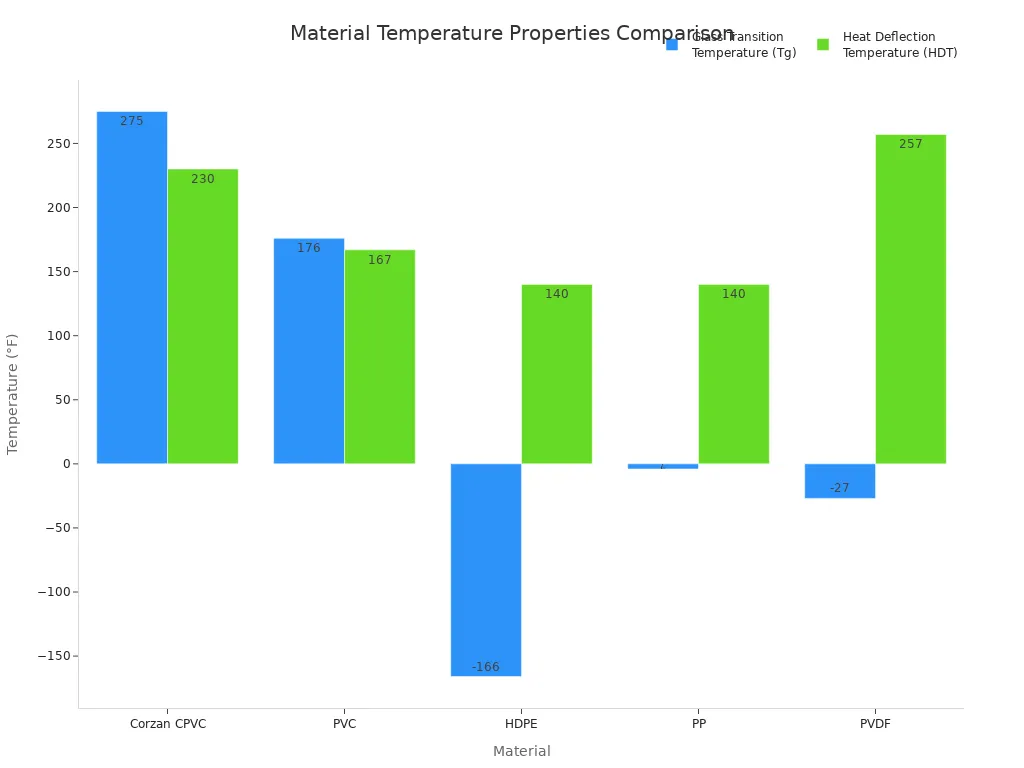
This chart clearly shows Corzan CPVC’s superior thermal resistance compared to PVC, HDPE, and PP.
Other Plastic Pipe Fittings and Their Niche Uses
Beyond PVC and CPVC, other plastic pipe fittings serve specific purposes in irrigation. High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) fittings offer excellent flexibility and impact resistance. Installers often use HDPE for main lines or in areas prone to ground movement. Polypropylene (PP) fittings resist many chemicals, making them suitable for systems handling fertilizers or other additives. However, these materials generally have lower maximum pressurized service temperatures, often around 140°F or 160°F. While some HDPE grades can handle up to 180°F, their pressure ratings at these elevated temperatures are significantly lower than CPVC. Each material has unique strengths, but for high-pressure and high-temperature demands, CPVC often stands out.
Chemical Resistance of PVC Pipe Fittings
High-pressure irrigation systems often encounter various chemicals, making the chemical resistance of PVC pipe fittings a critical factor. PVC demonstrates resistance to many substances commonly found in agricultural and water treatment applications. This includes alcohols, fats, oils, and certain acids, alkalis, and salts. Specifically, PVC is highly compatible with non-reactive chemicals such as Acetylene, various alcohols, Ammonia, ammonium salts, and antifreeze.
PVC’s molecular structure provides inherent stability. It does not contain iron or other metals that can oxidize, which prevents rust and corrosion. This material effectively resists acids, bases, salts, and other corrosive substances frequently present in water systems. For instance, PVC performs exceptionally well in harsh environments like coastal areas with salt air and industrial sites. Agricultural irrigation systems particularly benefit from PVC fittings due to their resistance to fertilizers and pesticides. These chemicals might otherwise degrade metal pipes, leading to premature failure.
However, chemical resistance can vary. Factors such as the specific type of chemical, its concentration, and the operating temperature significantly influence PVC’s performance. Unplasticized PVC generally offers superior chemical resistance compared to plasticized PVC. Users should also note that resistance can decrease at elevated temperatures, with a maximum threshold of 140°F for optimal chemical integrity. For comprehensive details on chemical compatibility, industry resources like the Plastics Pipe Institute’s Technical Report TR-19 and Uni-Bell’s Handbook of PVC Pipe Design and Construction provide extensive charts.
Decoding Pressure Ratings for PVC Pipe Fittings

PSI and Its Relevance to PVC Pipe Fittings
PSI, or Pounds per Square Inch, measures pressure in PVC pipes. It shows the force a pipe can withstand before failure. A higher PSI rating means the pipe handles greater internal pressure. This directly relates to its ability to resist bursting. Several factors influence this pressure rating. Temperature is one key factor. As the fluid’s temperature increases, the pressure capacity of PVC pipes decreases. PVC becomes softer and more flexible at higher temperatures. This makes it more likely to deform or fail under pressure. For example, a Schedule 40 PVC pipe rated for 450 PSI at 73°F might only be rated for 200 PSI at 140°F. Wall thickness is another critical factor. Thicker walls allow the pipe to handle more internal pressure. They absorb and distribute pressure more effectively. This reduces the risk of bursting.
Schedule (40, 80) and Wall Thickness of PVC Pipe Fittings
The terms Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 refer to the wall thickness of PVC pipe fittings. This difference in wall thickness directly impacts the pipe’s pressure rating. Schedule 40 PVC has a thinner wall compared to Schedule 80 PVC. Consequently, Schedule 40 has a lower pressure rating. Schedule 80 fittings, with their thicker walls, offer superior strength. They can withstand higher pressures. Engineers select the appropriate schedule based on the system’s specific pressure demands.
SDR (Standard Dimension Ratio) and Pressure Capacity of PVC Pipe Fittings
The Standard Dimension Ratio, or SDR, is another important factor for rating pressure pipes. SDR is calculated by dividing the pipe’s outside diameter (D) by its wall thickness (s): SDR = D / s. This ratio directly correlates with the pipe’s pressure capacity. A high SDR indicates a thin pipe wall relative to its diameter. This results in a low-pressure rating. Conversely, a low SDR signifies a thick pipe wall relative to its diameter. This leads to a high-pressure rating. For example, an SDR 9 pipe has a much thicker wall and higher pressure rating than an SDR 32.5 pipe of the same diameter. The dimensional ratio, including SDR values like 9, 11, 13.5, 17, 21, 26, and 32.5, determines a pipe’s pressure class. Interestingly, for the same material, dimension ratio, and application, the pressure rating of a pipe remains consistent even as its diameter changes.
Importance of Safety Margins for PVC Pipe Fittings
Implementing adequate safety margins for PVC pipe fittings is paramount in high-pressure irrigation systems. A safety margin provides a buffer against unexpected stresses and ensures the system operates reliably over its lifespan. It accounts for variables like pressure fluctuations, temperature changes, and potential water hammer effects. Ignoring these margins significantly increases the risk of system failure.
Manufacturers design PVC pipes with specific safety factors to ensure their integrity. For instance, PVC Pipe C900 (4”-12”) used in distribution mains typically incorporates a safety factor of 2.5 against its projected tensile strength. Larger PVC Pipe C905 (14” – 48”) for transmission mains often uses a safety factor of 2.0. These factors provide a robust cushion beyond the expected operating conditions.
| Pipe Type | Application | Safety Factor (against projected tensile strength) |
|---|---|---|
| PVC Pipe C900 (4”-12”) | Distribution Mains | 2.5 |
| PVC Pipe C905 (14” – 48”) | Transmission Mains | 2.0 |
| Plastic Pipe Materials | Long-term (50-year) tensile strength | Considered a ‘true’ Safety Factor derived from ultimate strength |
A pipe’s pressure rating indicates its maximum safe operating pressure, not its bursting point. This rating already includes a safety factor, usually 2.0. It also considers several critical aspects:
- Pipe diameter and wall thickness
- Material strength
- Temperature range
For irrigation pipes, engineers recommend reserving safety margins to account for water hammer effects. Water hammer occurs when water flow suddenly stops or changes direction, creating a pressure surge. This surge can momentarily exceed the system’s normal operating pressure. The pressure level of fittings must match the system’s working pressure, and the added safety margin protects against these transient spikes. This proactive approach prevents costly repairs and ensures continuous, efficient irrigation.
Durability Factors for PVC Pipe Fittings Beyond Pressure
UV Resistance of PVC Pipe Fittings
Sunlight significantly impacts the longevity of PVC pipe fittings. Prolonged exposure to UV rays causes PVC to yellow, fade, and discolor. This exposure also makes the material brittle and prone to cracks, compromising its structural integrity. Over time, UV degradation reduces PVC’s tensile strength and impact resistance. The outer layer of PVC breaks down, resulting in a chalky, rough surface. To prevent this deterioration, manufacturers engineer UV-resistant PVC pipes and fittings with UV inhibitors. These specialized products maintain structural integrity, resisting cracks, fading, and brittleness. Burying pipes underground or applying UV-resistant coatings also protects them from harmful rays, extending their lifespan.
Impact Resistance of PVC Pipe Fittings
Impact resistance measures a material’s ability to withstand sudden force without breaking. While specific Izod impact strength ratings for standard PVC pipe fittings are not widely published, this property remains crucial for durability. CPVC (Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride), a related material, offers enhanced impact resistance. For example, CPVC classified by ASTM D1784 with a ‘4’ in its second number indicates an Izod impact strength greater than 5 lbs. This characteristic is vital for fittings in environments where physical stress or accidental impacts might occur. Choosing materials with good impact resistance helps prevent damage during installation and operation.
Temperature Effects on PVC Pipe Fittings Performance
Temperature significantly affects the performance and durability of PVC pipe fittings. Standard PVC pipes generally withstand temperatures up to 140°F (60°C) without significant degradation. However, as temperatures rise above this threshold, PVC begins to soften and lose structural integrity. Its pressure rating decreases substantially. For instance, at 160°F (71°C), PVC’s pressure rating reduces to 50% of its rating at 73°F (23°C). At 200°F (93°C), PVC cannot withstand any pressure and will likely fail.
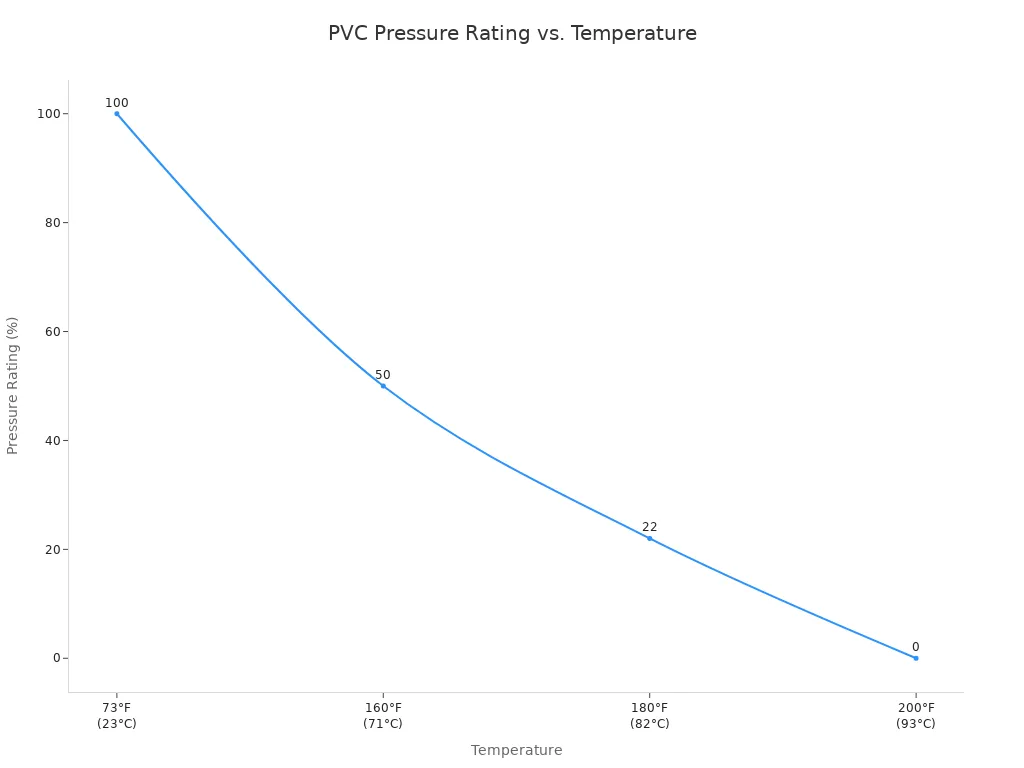
Freezing temperatures also pose challenges. PVC becomes more brittle in cold conditions, increasing its susceptibility to impact damage. If water inside the pipe freezes, the expanding ice can cause the pipe to burst. Additionally, PVC pipes expand and contract with temperature changes. Designers must account for this thermal expansion and contraction during installation to prevent stress on the system. CPVC, a modified version of PVC, offers superior temperature resistance, typically handling continuous use up to 200°F (93°C).
Installation Techniques for Long-Lasting PVC Pipe Fittings
Proper installation significantly extends the lifespan of PVC pipe fittings in high-pressure irrigation systems. Incorrect techniques can lead to leaks, reduced efficiency, and premature system failure. Solvent welding is a common and effective method for joining PVC pipes and fittings. This process creates a strong, permanent bond.
Installers must follow specific steps for successful solvent welding:
-
Prepare the Pipe and Fittings:
- Cut the pipe squarely. Use ratchet cutters, wheel cutters, or a fine-tooth saw. For existing pipes, cut at least two inches beyond any visible damage.
- Remove burrs or filings from the pipe. Bevel the pipe end with a chamfering tool. This streamlines assembly and ensures leak-free joints.
- Wipe away dirt and moisture.
- Check the fit: The pipe should contact the socket wall one-third to two-thirds of the way in. Discard the fitting if the pipe goes all the way in without resistance.
-
Apply Primer:
- Apply a heavy, even coat of solvent primer inside the fitting socket. Keep the surface wet until softened. Drain any puddles.
- Apply primer one-half inch beyond the fitting socket depth on the pipe end.
- Apply a second coat of primer to the fitting socket.
-
Apply Solvent Cement:
- Shake cement containers well before use.
- Apply a heavy, even layer on the pipe end.
- Apply a medium layer into the fitting socket.
- Apply a second heavy layer on the pipe end. Ensure proper coverage to avoid gaps or excessive softening. The application tool (swab or roller) should be half the size of the pipe diameter.
-
Assemble the Joint:
- Immediately insert the pipe into the fitting. Use one smooth action until it reaches the stop.
- For sizes two inches and below, rotate the pipe one-quarter to one-half turn while inserting.
- Hold the assembly for approximately 30 seconds to set.
-
Verify Installation:
- An even bead of cement should be visible around the joint. If not, disassemble and remake the joint. This continuous bead is critical for system integrity.
For heavier, large-diameter pipes, use additional help for alignment and connection. A mechanical joining tool, like a pipe puller, ensures accurate and secure solvent welds. It seats pipes completely. Consider prefabricating joints whenever possible. This reduces on-site work, especially for complex installations.
Selecting Specific PVC Pipe Fitting Types for Applications

Couplings and Adapters for Secure PVC Pipe Fittings Connections
Couplings and adapters play a crucial role in high-pressure irrigation systems. Couplings connect two pipes of the same diameter, creating a continuous line. Adapters join pipes of different sizes or connect pipes to other system components like valves or pumps. Installers use slip couplings for permanent solvent-welded connections. Threaded adapters allow for disassembly and maintenance. Selecting the correct type ensures a leak-proof and robust system. These components must match the pressure rating of the pipes they connect to maintain system integrity.
Elbows and Tees for Directional Changes with PVC Pipe Fittings
Elbows and tees manage directional changes and branching in irrigation lines. Elbows create turns, typically at 45 or 90 degrees. Tees allow a single line to split into two, often at a 90-degree angle. These fittings introduce some flow restriction, which can impact system pressure. Different types of elbows and tees have varying flow restriction coefficients.
| Fitting | Fitting Type | Range of Variation |
|---|---|---|
| 90 Deg. Elbow | Regular Screwed | ± 20 percent above 2 inch size |
| Regular Screwed | ± 40 percent above 2 inch size | |
| Long Radius, Screwed | ± 25 percent | |
| Regular Flanged | ± 35 percent | |
| Long Radius, Flanged | ± 30 percent | |
| 45 Deg. Elbow | Regular Screwed | ± 10 percent |
| Long Radius, Flanged | ± 10 percent | |
| Tee | Screwed, Line or Branch Flow | ± 25 percent |
| Flanged, Line or Branch Flow | ± 35 percent |
Engineers consider these variations when designing systems to minimize pressure loss. Long-radius elbows offer less resistance than regular elbows. Choosing appropriate fittings helps maintain consistent pressure throughout the irrigation network.
Valves for Control in High-Pressure PVC Pipe Lines
Valves provide essential control over water flow in high-pressure irrigation systems. They allow operators to start, stop, or regulate the flow to different sections. Ball valves offer quick shut-off capabilities. Gate valves provide a full-bore flow path with minimal pressure drop when fully open. Globe valves offer precise flow regulation. Each valve type serves a specific purpose. Selecting valves with appropriate pressure ratings ensures safe and efficient operation. Proper valve placement allows for isolation of sections for maintenance or repair without shutting down the entire system.
Threaded vs. Solvent Weld PVC Pipe Fittings for High Pressure
Choosing the right connection method for PVC pipe fittings significantly impacts system integrity, especially in high-pressure irrigation. Two primary methods exist: threaded connections and solvent weld connections. Each offers distinct advantages and disadvantages.
Solvent welding creates a permanent, chemically fused joint. This method involves applying a primer and then a solvent cement to both the pipe and the fitting. The cement softens the PVC surfaces, allowing them to chemically bond together. This process forms a single, homogeneous piece of plastic. Solvent-welded joints are exceptionally strong and leak-proof. They maintain the full pressure rating of the pipe itself. For high-pressure applications, experts widely recommend solvent welding. It provides the most reliable and durable connection.
Threaded PVC fittings, conversely, offer convenience for assembly and disassembly. Installers screw these fittings onto threaded pipe ends. This method is useful for sections requiring future maintenance or modification. However, threaded connections introduce potential weaknesses in high-pressure systems. The threading process removes material from the pipe wall, reducing its thickness and thus its pressure rating. This reduction makes threaded joints more susceptible to leaks or failure under high internal pressure.
⚠️ Caution: Always apply thread sealant (like PTFE tape or pipe dope) to threaded PVC connections. This helps prevent leaks and reduces friction during assembly. However, even with sealant, threaded joints typically do not match the pressure integrity of solvent-welded joints.
For high-pressure irrigation, solvent welding is generally the superior choice. It ensures maximum strength and reliability. Threaded fittings are best reserved for lower-pressure zones or areas where periodic disconnection is essential. Engineers prioritize the robust, permanent bond of solvent welding to prevent costly failures in demanding irrigation environments.
Practical Steps for Choosing Your PVC Pipe Fittings
Choosing the correct components for a high-pressure irrigation system requires careful consideration. Engineers must evaluate several key factors to ensure system longevity and efficiency. This section outlines practical steps for making informed decisions.
Assessing System Operating Pressure for PVC Pipe Fittings
Accurately determining the system’s operating pressure is the first critical step. This assessment ensures all components, including fittings, can safely handle the demands placed upon them. Operators can measure system pressure using standard pressure gauges. These gauges are readily available in various ranges, such as 15, 30, 60, or 100 psi (100, 200, 400, or 700 kPa). Selecting a gauge with an accuracy range suitable for the pump’s maximum pressure is important. For example, a 60-psi gauge works well for a pump producing up to 50 psi.
For a more comprehensive analysis, operators use a head-discharge measurement apparatus. This setup includes a pressure gauge, a flow meter, and a regulating valve. Install this apparatus on a straight pipe section. The pipe length must meet the flow meter manufacturer’s specifications for accuracy. This often means 10 pipe diameters upstream and 6 downstream, though straightening vanes can reduce this requirement. All components must be appropriately sized and pressure-rated for the pump’s full operating range.
To measure pressure accurately:
- Connect the head-discharge apparatus to the pump discharge. Ensure sufficient straight pipe lengths for accurate flow rate measurement.
- Operate the pump to remove air and achieve normal operating conditions.
- Slowly close the regulating valve to measure the shut-off head. This represents the maximum pressure with no flow. Ensure all components can withstand this pressure.
- Open the regulating valve slightly. Record both the pressure and the flow rate.
- Repeat the previous step at various valve openings. Collect at least 6 to 8 data points across the pump’s flow range.
- For convenience, adjust the regulating valve to achieve uniform pressure changes. For example, use 5 psi decrements. Measure the corresponding discharge rates until the valve is fully open.
This detailed assessment provides the necessary data to select fittings with appropriate pressure ratings.
Environmental Factors Affecting PVC Pipe Fittings
The environment where an irrigation system operates significantly influences the durability of its components. Designers must consider several environmental factors. Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight can degrade PVC. This causes it to become brittle and crack over time. For above-ground installations, using UV-resistant fittings or protecting them with coatings or burial is essential.
Temperature fluctuations also impact performance. Extreme cold can make PVC more brittle, increasing its susceptibility to impact damage. High temperatures reduce PVC’s pressure rating and can lead to softening. System designers must select materials rated for the expected temperature range. Soil conditions also play a role. Abrasive soils can cause external wear on buried pipes. Corrosive soil chemicals might affect certain pipe materials, though PVC generally exhibits good resistance. Finally, consider potential physical impacts from agricultural machinery, animals, or human activity. Choosing fittings with good impact resistance helps prevent damage in these scenarios.
Evaluating Chemical Compatibility of PVC Pipe Fittings
High-pressure irrigation systems often deliver more than just water. They frequently carry fertilizers, pesticides, and other agricultural chemicals. Therefore, evaluating the chemical compatibility of fittings is crucial. PVC generally offers good resistance to many common chemicals. However, specific chemical compositions and concentrations can affect its integrity.
For instance, PVC shows excellent tolerance to certain substances:
| Chemical | Tolerance/Effect |
|---|---|
| Ammonia Nitrate | B-Good |
| Ammonium Nitrate | A2-Excellent |
A rating of ‘A2-Excellent’ indicates the material is highly suitable for continuous contact with the chemical. A ‘B-Good’ rating suggests suitability, but monitoring the system for any signs of wear over time is advisable.
PVC is generally suitable for irrigation pipes that may be exposed to fertilizers and pesticides. However, always consult a suitability chart to ensure the material can handle such exposure. Different chemicals, their concentrations, and operating temperatures can all influence PVC’s resistance. Always verify the compatibility of all chemicals used in the system with the chosen fitting material. This proactive approach prevents material degradation, leaks, and potential system failures.
Consulting Manufacturer Specifications for PVC Pipe Fittings
Consulting manufacturer specifications is a non-negotiable step when selecting PVC pipe fittings for high-pressure irrigation. These documents provide critical data. They ensure the chosen components meet the system’s exact requirements. Manufacturers rigorously test their products. They publish detailed information about performance capabilities. Ignoring these specifications can lead to system failure.
Designers must review several critical parameters in manufacturer specifications. These parameters include:
- PN Rating (Pressure Nominal): This rating defines the internal pressure a pipe can safely handle at a standard temperature, for example, PN10, PN16, or PN20.
- Wall Thickness: This factor significantly influences the pipe’s pressure handling capability. Thicker walls withstand higher pressures.
- Material: Differentiating between PVC and UPVC is crucial. This distinction affects performance characteristics.
- Nominal Pipe Size: This parameter, along with wall design, determines the pressure a pipe can withstand.
- Application: Identifying the intended use, such as domestic plumbing or industrial flow, guides selection.
- Working Pressure: The normal operating pressure of the system must be measured and considered.
- Temperature Considerations: The pressure rating is typically specified at a standard temperature, often 20°C. Variations in temperature can significantly affect performance.
- Manufacturer Standards: Adhering to these standards ensures compliance and safety.
- UV Exposure: Consideration for outdoor installations is vital to prevent degradation from sunlight.
- Corrosion Environment: Assessing the environment ensures material compatibility and longevity.
Manufacturers also provide guidelines for installation, chemical compatibility, and temperature de-rating factors. Following these guidelines ensures optimal performance and extends the lifespan of the irrigation system. Always cross-reference the system’s operational demands with the manufacturer’s stated capabilities.
Balancing Budget and Long-Term Performance of PVC Pipe Fittings
Balancing the initial budget with long-term performance is a critical decision for any high-pressure irrigation project. While lower-cost options might seem appealing initially, they often lead to higher expenses over time. Investing in higher-quality PVC pipe fittings from the start prevents costly repairs and replacements down the road.
High-quality PVC pipes offer significant long-term value in irrigation infrastructure. Their stable molecular structure and anti-corrosion properties allow them to last 50 to 100 years under normal conditions. This durability eliminates replacement costs typical for metallic systems, which often require replacement every 10-15 years in corrosive environments. Proper installation and maintenance further extend this lifespan. Factors like water quality, water pressure, and UV exposure also influence longevity. High water pressure can stress pipes and fittings. This increases the risk of cracks or leaks. Therefore, selecting appropriate pipe grades like PN10 or PN16 based on system pressure is essential for safe and long-lasting use. Schedule 40 PVC is common for residential applications. Higher-pressure systems often require Schedule 80 PVC due to its increased wall thickness and pressure ratings.
The economic advantages of PVC extend beyond initial savings. PVC’s smooth interior surfaces maintain flow efficiency. This hydraulic efficiency reduces pumping costs. Leak-free joints prevent water loss, a significant cost in large-scale irrigation. Design flexibility allows optimization of system layout. This reduces the need for expensive fittings and special components. Quality PVC piping systems resist corrosion, cracking, and material breakdown. This ensures long-term performance. Leak-resistant pipes prevent unnecessary water loss. This makes irrigation efficient and sustainable. Strong materials lead to fewer repairs, saving time, labor, and money. Consistent water flow ensures crops receive the water they need. This contributes to efficient water distribution.
High-pressure PVC fittings are generally more affordable than metal counterparts. This applies to both initial investment and long-term maintenance. PVC’s lightweight nature reduces transportation and installation costs. The ease of installation for PVC means lower labor expenses compared to metal fittings. Metal fittings often require specialized tools and welding. Therefore, choosing high-quality PVC fittings provides the best return on investment. It reduces maintenance, conserves water, and keeps crops healthy.
💡 Tip: Always consider the total cost of ownership, not just the purchase price, when selecting PVC pipe fittings. Long-term savings from reduced maintenance and increased efficiency often outweigh initial cost differences.
Selecting the right components for high-pressure irrigation is a critical decision. It impacts system efficiency and longevity. By carefully considering material properties, understanding pressure ratings, and evaluating durability factors, you can ensure a robust and reliable irrigation system. This system will meet specific needs and avoid costly failures. Always prioritize fittings that exceed your system’s demands for optimal performance and peace of mind.
FAQ
What is the main difference between Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 PVC fittings?
Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 PVC fittings differ in wall thickness. Schedule 80 fittings have thicker walls than Schedule 40. This increased thickness allows Schedule 80 fittings to withstand higher internal pressures. Engineers select the appropriate schedule based on system pressure demands.
Why is CPVC sometimes preferred over standard PVC for irrigation?
CPVC pipe fittings offer superior performance in higher temperature environments. They withstand temperatures up to 200°F, significantly higher than standard PVC. CPVC also maintains its pressure rating better at elevated temperatures. This makes it ideal for systems with fluctuating water temperatures.
How does UV exposure affect PVC pipe fittings?
Prolonged UV exposure from sunlight degrades PVC. It causes the material to yellow, become brittle, and crack. This deterioration reduces the PVC’s tensile strength and impact resistance. Using UV-resistant fittings or protecting them from direct sunlight prevents this damage.
Is it better to use threaded or solvent weld connections for high-pressure PVC?
Solvent weld connections are generally superior for high-pressure PVC. They create a permanent, chemically fused joint, maintaining the pipe’s full pressure rating. Threaded connections reduce the pipe wall thickness, making them more susceptible to leaks or failure under high pressure.
What is the importance of a safety margin in PVC pipe pressure ratings?
A safety margin provides a buffer against unexpected stresses. It accounts for pressure fluctuations, temperature changes, and water hammer effects. This ensures the system operates reliably over its lifespan. Ignoring safety margins increases the risk of system failure and costly repairs.




