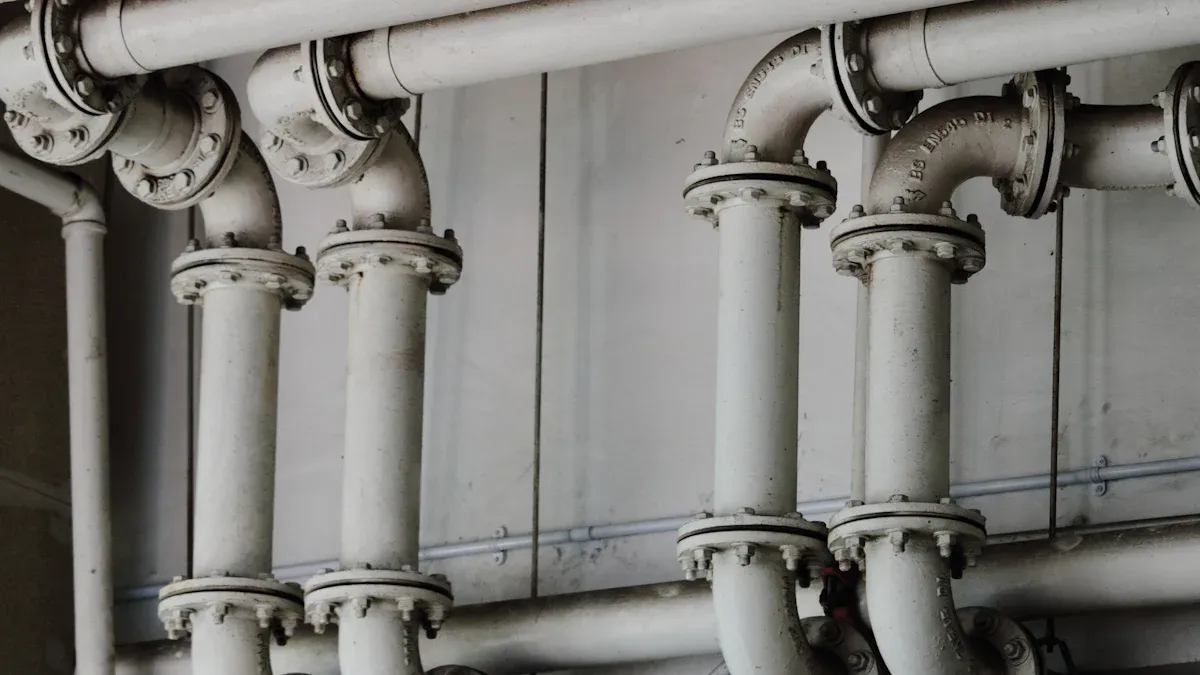

Selecting the correct HDPE pipe fittings is crucial for the integrity and longevity of any water supply system. Incorrect choices lead to significant issues, including ‘parrot’s beak failure’ in city networks, which causes costly downtime and repair expenses. The right water supply HDPE fittings ensure efficient water delivery and prevent such failures. Leaks at connection points, often due to improper installation, also highlight the importance of careful selection. This guide will help you navigate essential factors for informed decision-making, covering topics like HDPE fittings for irrigation systems and compatibility with other materials, such as PVC Pipe Fittings. Understanding what are the different types of PVC pipe fittings is also important for comprehensive system design.
Key Takeaways
- Choose the right HDPE pipe fitting type for your water system. Each type, like electrofusion or butt fusion, works best for different jobs.
- Match fittings to your system’s pressure needs and pipe size. Also, check if they can handle the water quality and outdoor conditions.
- Always pick fittings that meet industry standards. Look for certifications and choose trusted manufacturers to ensure quality.
- Properly prepare pipe joints before installation. Regular checks and upkeep help your water system last a long time.
Understanding HDPE Pipe Fitting Types and Their Applications

Choosing the correct HDPE pipe fitting type is fundamental for the success and longevity of any water supply system. Each fitting offers unique advantages and is best suited for specific applications. Understanding these differences helps engineers and installers make informed decisions.
Electrofusion Fittings for Precision Connections
Electrofusion fittings provide a highly reliable and precise method for joining HDPE pipes. These fittings contain integrated electrical heating coils. When an electric current passes through these coils, the material melts, creating a homogeneous and strong bond between the fitting and the pipe. This process ensures a leak-proof connection, which is especially critical in sensitive applications.
Electrofusion fittings are particularly valuable in situations demanding high integrity and where other fusion methods might be challenging. Their common applications include:
- Connecting pipes underground in municipal water systems.
- Connecting pipes in confined spaces within municipal water systems.
- Large-scale irrigation projects.
- New construction operations in municipal and industrial water systems.
- Rehabilitation operations in municipal and industrial water systems.
- Emergency repair operations in municipal and industrial water systems.
- Potable water supply systems.
- Irrigation networks.
- Main distribution lines in pressurized HDPE water systems.
- Lateral service branches in pressurized HDPE water systems.
- Zoned water distribution for diverting supply to multiple neighborhoods, facilities, or hydraulic circuits.
Butt Fusion Fittings for Strong, Seamless Joints
Butt fusion is a widely used method for creating strong, seamless joints in HDPE piping systems. This technique involves heating the ends of two pipes or a pipe and a fitting to a molten state. Workers then press the heated surfaces together under controlled pressure. This process creates a homogeneous joint that is as strong as, or even stronger than, the pipe itself. Butt fusion is ideal for long runs of pipe and large-diameter applications where a continuous, robust pipeline is essential.
Butt fusion welded joints demonstrate impressive strength. They can achieve a tensile strength of up to 80% of the original pipe material. Several factors influence the actual tensile strength. These include the quality of the welding process, the specific type of HDPE material used, the pipe’s diameter and wall thickness, and the environmental conditions where the joint will be utilized. This method is a cornerstone for creating durable and reliable water infrastructure.
Compression Fittings for Smaller Diameter Pipes
Compression fittings offer a quick and easy solution for connecting HDPE pipes, especially for smaller diameters. These fittings do not require specialized fusion equipment or heat. Instead, they create a seal by compressing a gasket or O-ring around the pipe when a nut is tightened. This mechanical connection makes them highly convenient for repairs or installations where fusion equipment is impractical.
Compression fittings are particularly suitable for specific pipe dimensions. NORMA® Compression fittings, for example, are designed for polyethylene tubing with diameters ranging from 16 to 110 mm. These fittings are often suitable for non-potable water applications. Manufacturers typically construct them from polypropylene, making them compatible with both high- and low-density polyethylene tubing. Their ease of installation makes them a popular choice for various smaller-scale projects.
Mechanical Fittings for Versatility and Disassembly
Mechanical fittings offer a flexible solution for connecting HDPE pipes. They do not require heat or specialized fusion equipment. Instead, these fittings use a mechanical seal, often involving gaskets, bolts, and clamps. This design allows for easy assembly and disassembly. Installers find them particularly useful for temporary setups or sections of a system that may need future modification. They also simplify repairs, as workers can quickly replace a damaged section without extensive re-fusion. Their versatility makes them a valuable option in various water supply applications.
Transition Fittings for Connecting to Other Materials, Including PVC Pipe Fittings
Water supply systems often require connections between HDPE pipes and other materials. Transition fittings bridge these different pipe types. They ensure a secure and leak-proof connection between dissimilar materials. Common connections include HDPE to metal pipes or HDPE to PVC Pipe Fittings. Selecting the correct transition fitting is crucial for system integrity, especially when dealing with various PVC Pipe Fittings.
Some fitting types, like electrofusion and compression fittings, can also function as transition fittings in specific scenarios. Electrofusion fittings, for example, create strong, reliable joints by melting embedded wires. They can connect pipes of different diameters or materials, finding use in water distribution and industrial applications. Compression fittings offer a quick, heat-free way to connect HDPE pipes. They use a compression ring and nut for a secure seal, often appearing in low-pressure water supply and irrigation systems.
For connecting HDPE PE 4710 to PVC Schedule 40/80 piping systems, specialized solutions exist. The Series 730 Transition Fitting by Poly-Cam provides a dedicated option. This fitting uses hydraulic-press technology and robust materials. It ensures leak-free performance in potable water, gas distribution, and high-pressure industrial applications. This specific fitting works for both above-ground and buried installations. It offers versatile coupling options, including Epoxy-Coated Carbon Steel, 304/316 stainless steel, and ERW Pipe. The materials are certified, including HDPE PE 4710 and NSF-approved PVC Sch. 40/80. A leak-proof radial compression system with a multi-level barb ensures reliability. This fitting supports dual installation methods. Workers can use butt fusion or electrofusion for the HDPE end. They use solvent cement for the PVC end. This ensures a robust connection to PVC Pipe Fittings. When integrating HDPE with PVC Pipe Fittings, choosing the right transition piece prevents compatibility issues and maintains system performance. Understanding the nuances of connecting to PVC Pipe Fittings is essential for a hybrid system.
Key Factors for Selecting HDPE Fittings
Selecting the correct HDPE fittings requires careful consideration of several critical factors. These factors directly impact the system’s performance, longevity, and safety. Engineers and installers must evaluate each aspect to ensure optimal functionality.
Matching Fittings to System Pressure Requirements
System pressure requirements represent a primary consideration when choosing HDPE fittings. Every fitting possesses a specific pressure rating, indicating the maximum internal pressure it can safely withstand. Installers must select fittings with a pressure rating equal to or greater than the maximum operating pressure of the water supply system. Exceeding a fitting’s pressure rating can lead to catastrophic failures, including leaks, bursts, and system downtime. Manufacturers typically specify pressure ratings using terms like PN (Nominal Pressure) or PSI (Pounds per Square Inch). Matching these ratings precisely ensures the integrity and safety of the entire pipeline.
Ensuring Compatibility with Pipe Diameter and SDR Ratio
Compatibility between fittings and pipes extends beyond just matching the nominal diameter. The Standard Dimension Ratio (SDR) also plays a crucial role. The SDR defines the ratio of the pipe’s outside diameter to its wall thickness. A lower SDR value indicates a thicker pipe wall, which generally corresponds to a higher pressure rating. Fittings must precisely match both the diameter and the SDR of the pipe they connect. A mismatch in SDR can create weak points in the pipeline, even if the diameter appears correct. This mismatch compromises the joint’s strength and the overall system’s ability to handle pressure. Proper SDR matching ensures a consistent wall thickness across the joint, which is vital for successful fusion and long-term reliability.
Considering Water Quality and Chemical Compatibility
The quality of the water flowing through the system significantly influences fitting selection. Water can contain various substances, including minerals, dissolved solids, and treatment chemicals like chlorine. These substances can interact with pipe materials over time. Therefore, assessing the chemical compatibility of HDPE fittings with the specific water quality is essential.
HDPE fittings offer excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals. This property makes them highly suitable for many water supply applications.
- HDPE fittings exhibit high resistance to chemicals.
- They can withstand corrosive substances.
- They are resistant to acids.
- They are resistant to bases.
This inherent chemical resistance ensures that fittings do not degrade when exposed to common water treatment chemicals or naturally occurring corrosive elements in the water. This characteristic helps maintain the purity of the water and extends the service life of the entire system.
Assessing Environmental Conditions and UV Exposure
Environmental conditions significantly impact the long-term performance of HDPE fittings. Exposure to sunlight, especially ultraviolet (UV) radiation, can degrade the material over time. UV radiation causes photodegradation in HDPE pipes. This process breaks chemical bonds in the polymer chains. The pipe becomes more brittle and prone to cracking under stress. The surface can also fade and become chalky, indicating damage to the outer layer.
Factors influencing UV resistance include additives like carbon black. Carbon black absorbs and scatters UV radiation. Pipe thickness also plays a crucial role. Thicker pipes offer more material to absorb UV energy. Exposure conditions, such as intensity and duration of sunlight, also significantly affect the extent of degradation. Increased aging time and sunlight exposure intensity lead to a decrease in mechanical and chemical properties. The oxidation degradation mechanism involves chain scission and oxidation primarily in the amorphous regions. The depth of oxidation is less than 50 μm from the surface.
A study evaluated recycled and virgin HDPE corrugated pipes under 3600 hours of accelerated UV aging. Both types maintained good properties. UV radiation did not significantly affect them. Statistical analysis showed no significant difference in tensile strength, elastic modulus, and hardness measurements before and after UV exposure. This resilience was attributed to the addition of carbon black, antioxidants, and UV stabilizers. These additives prevented further aging. Therefore, selecting fittings with appropriate UV stabilizers and carbon black content is crucial for outdoor or exposed installations.
Practical Considerations for Installation Methods
The chosen installation method directly influences the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of a water supply system. Different fitting types require specific installation techniques. Each technique has its own practical considerations.
Butt fusion equipment is relatively simple to operate. The welding process is easy to master. This makes it suitable for on-site installation. It simplifies the process by not requiring additional materials or fittings. Butt fusion is generally faster than electrofusion for similar pipe sizes. This method is ideal for long, continuous pipe runs.
Electrofusion offers high reliability and ease of operation. This can lead to savings in time and labor costs, especially in complex projects. Electrofusion can be automated for large-scale projects. This helps in reducing labor costs. It is particularly useful in confined spaces or when connecting pipes of different diameters. Mechanical fittings, on the other hand, do not require specialized equipment. Workers can install them quickly. This makes them suitable for temporary setups or repairs where speed is essential. Compression fittings also offer quick, heat-free connections. They are often used in low-pressure water supply and irrigation systems.
Choosing the right installation method depends on project scale, site conditions, and available resources. Understanding the nuances of each technique ensures a smooth and efficient installation process.
Ensuring Quality and Compliance in HDPE Fittings
Ensuring the quality and compliance of HDPE fittings is paramount for the long-term reliability of any water supply system. Engineers must select products that meet stringent industry standards and come from reputable manufacturers. This approach guarantees the integrity and safety of the entire pipeline.
Adherence to Industry Standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO)
Adherence to industry standards ensures the consistent quality and performance of HDPE fittings. Several key standards govern the manufacturing and performance of these components. For instance, ISO 4427-3 specifically addresses fittings for polyethylene piping systems used in water supply. EN 12201-3 also covers fittings for plastics piping systems in water supply. Other relevant standards include ISO 17885 for mechanical fittings, ISO 9623 for PE/metal and PP/metal adapter fittings, and ISO 9624 for flange adapters.
ISO 4427:2019 specifies requirements for materials, dimensions, performance, and testing methods for HDPE pipes in water supply. It mandates the use of PE80 or PE100 grade high-density polyethylene raw materials. ASTM D3350-24 regulates the raw material performance of HDPE pipes through a classification system. This system covers properties like density, melt flow rate, and flexural modulus. EN 12201 covers HDPE piping systems for both drinking and non-drinking water. It includes requirements for materials, connection methods, and long-term performance.
Importance of Manufacturer Reputation and Certifications
A manufacturer’s reputation and certifications directly reflect the quality and reliability of their HDPE fittings. Certifications provide independent verification that products meet specific safety and performance criteria. For potable water applications, certain certifications are essential. NSF/ANSI/CAN 61 ensures materials in contact with drinking water are safe in the USA and Canada. WRAS approves fittings that comply with UK drinking water quality regulations. DVGW certifies fittings for potable water systems in Germany.
NSF/ANSI 61 Certification requires HDPE fittings to pass chemical leaching tests. These tests ensure no excessive release of heavy metals or plastic additives. WRAS Certification ensures products comply with the UK’s water fittings regulations. It prevents products from wasting or polluting water sources. DVGW Certification sets European benchmarks for material safety and hygiene in drinking water systems.
Matching Material Grade of Fittings to Pipe Specifications
Matching the material grade of fittings to pipe specifications is critical for creating a homogeneous and strong system. HDPE pipes come in different material grades, such as PE80 and PE100. These grades have distinct properties, including pressure ratings and long-term strength. Fittings must correspond to the specific grade of the pipe they connect. A mismatch can lead to weak points in the system. It compromises the joint’s integrity and the overall pressure-bearing capacity. Proper material grade matching ensures optimal performance and longevity for the entire water supply network.
Best Practices for HDPE Pipe Fitting Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation and consistent maintenance are vital for the long-term performance of any HDPE water supply system. Following best practices ensures the system’s integrity and prevents costly failures.
Proper Joint Preparation and Fusion Techniques
Effective joint preparation is the cornerstone of a strong HDPE connection. Pipe and fitting surfaces must be properly prepared, clean, and dry before welding. This meticulous preparation ensures a reliable and leak-proof joint.
For electrofusion and butt fusion, specific steps are crucial:
- Clean the Elements to be Welded: Workers remove mud, dust, grease, or other impurities. They use water and a clean, lint-free cloth or soft paper soaked in a suitable detergent. Avoid solvents like trichloroethylene, denatured alcohol, or gasoline.
- Cut the Ends to Weld: Use appropriate pipe cutters or equipment with a fixed-guide blade. This ensures flat and square cuts. Deburr the outer edge and chamfer if necessary.
- Mark the Scraping Area: Mark at least one-third of the pipe’s circumference. The scraped length should exceed the electrofusion fitting’s insertion depth by at least 10 mm.
- Remove the Oxidized Surface Layer: Use suitable manual or mechanical scrapers. This removes the oxidized layer (approximately 0.1 mm for pipes up to dn 63 mm, 0.2 mm for pipes dn 63 mm or more). Do not use sandpaper, emery cloth, or rasps. Do not scrape the electrofusion fitting.
- Clean Scraped Surfaces: Clean pipe ends again with a suitable detergent. This removes polyethylene residue or dust. Ensure all surfaces are completely dry. Only remove the electrofusion fitting from its protective packaging just before welding.
- Mark the Insertion Depth: Mark the insertion depth on at least one-third of the pipe ends’ circumference. This depth equals half the electrofusion fitting’s length.
- Insert the elements to be welded into the Fitting: Insert pipes without forcing. Ensure perfect coaxiality using aligners. Check for ovalization if insertion is difficult. Observe depth marks.
For butt fusion, after cleaning, workers align and clamp the two pipe ends. They ensure a seamless transition without gaps. The fusion machine’s facing tool creates a clean, smooth, virgin HDPE surface. After facing, workers clear excess pipe shavings. They avoid touching the clean ends to prevent contamination.
Regular Inspection and Maintenance for System Longevity
Regular inspection and maintenance routines extend the lifespan of HDPE water supply systems. System operators should schedule periodic checks for visible signs of wear, damage, or leaks. They pay close attention to joints and connections, as these areas are often vulnerable. Early detection of issues allows for timely repairs, preventing minor problems from escalating into major failures. Maintaining accurate records of inspections and repairs helps track system health over time. This proactive approach ensures continuous, efficient water delivery.
Careful selection of HDPE pipe fittings builds a robust water supply system. This ensures system integrity. Engineers must consider fitting types, system requirements, and environmental factors. This leads to optimal performance. Consulting professionals ensures system integrity for complex installations. They provide expert guidance.
FAQ
What is the main difference between electrofusion and butt fusion?
Electrofusion uses integrated heating coils to melt and join pipes. This creates a precise, strong bond. Butt fusion heats pipe ends and presses them together. This forms a seamless, homogeneous joint. Both methods create reliable connections.
Can HDPE fittings connect to PVC pipes?
Yes, specialized transition fittings connect HDPE pipes to PVC pipes. These fittings ensure a secure, leak-proof connection between the different materials. They are crucial for hybrid water supply systems.
Why is SDR important when choosing fittings?
SDR (Standard Dimension Ratio) indicates a pipe’s wall thickness relative to its diameter. Matching the fitting’s SDR to the pipe’s SDR is crucial. This ensures consistent strength and pressure rating across the joint.
Are HDPE fittings safe for drinking water?
Yes, many HDPE fittings are safe for drinking water. They must meet specific certifications like NSF/ANSI/CAN 61 or WRAS. These certifications ensure the materials do not leach harmful substances into the water.
How does UV exposure affect HDPE fittings?
UV radiation can degrade HDPE over time. This makes the material brittle. Fittings for outdoor use often contain UV stabilizers and carbon black. These additives protect against sun damage and ensure longevity.




